Proccesors: The New Era.
What is a proccesor?
The proccesor is part of the hardware system and its the brain of the computer.
A processor is the logic circuitry that responds to and processes the basic instructions that drive a computer. The four primary funcions of a processor are fetch, decode, execute and writeback.
The parts of the proccesor:
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which carries out arithmetic and logic operations on the operands in instructions
The floating point unit (FPU), also known as a math coprocessor or numeric coprocessor, a specialized coproccesor that manipulates numbers more quickly than the basic microprocessor circuitry can.
Registers, which hold instructions and other data. Registers supply operands to the ALU and store the results of operations.
L1 and L2 cache memory Their inclusion in the CPU saves time compared to having to get data from random access memory (RAM).
What proccesor would be the good one?
There are many proccesors on the market, but deppending on the user needs can be better ton informate correctly.
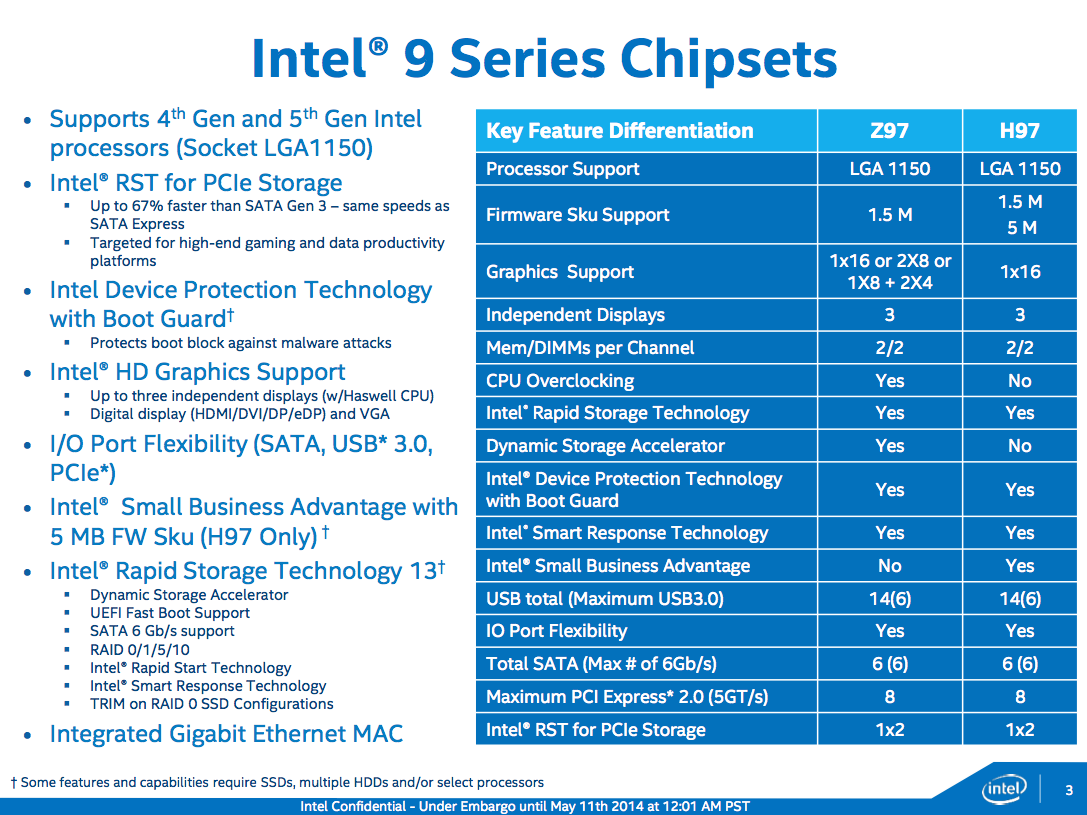
I left here for you a chart with the new: INTEL 9 SERIES CHIPSETS.
A microprocessor is a computer processor that incorporates the functions of a central processing unit on a single integrated circuit (IC),[1] or at most a few integrated circuits.[2] The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock driven, register based, digital-integrated circuit that accepts binarydata as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic. Microprocessors operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary numeral system.
Motherboard:
A motherboard (sometimes alternatively known as the main circuit board, system board, baseboard, planar board or logic board,[1] or colloquially, a mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) found in general purpose microcomputers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general purpose use and applications.
Microprocessor:
Structure:
The internal arrangement of a microprocessor varies depending on the age of the design and the intended purposes of the microprocessor. The complexity of an integrated circuit (IC) is bounded by physical limitations on the number of transistors that can be put onto one chip, the number of package terminations that can connect the processor to other parts of the system, the number of interconnections it is possible to make on the chip, and the heat that the chip can dissipate.
Intel Core i5-7600K. Like the 7700K that preceded it on this list, the Intel Core i5-7600K is an unlocked, overclockable quad-core processor fromIntel. However, it also suffers from the same integral shortcoming; that is that it's barely an upgrade over the i5-6600K.
Random-access memory:
Random-access memory (RAM /ræm/) is a form of computer data storage that stores data and machine code currently being used. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory. In contrast, with other direct-access data storage media such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWsand the older magnetic tapes and drum memory, the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.
Types of random-access memory:
The two widely used forms of modern RAM are static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM (DRAM). In SRAM, a bit of data is stored using the state of a six transistor memory cell. This form of RAM is more expensive to produce, but is generally faster and requires less dynamic power than DRAM. In modern computers, SRAM is often used as cache memory for the CPU. DRAM stores a bit of data using a transistor and capacitor pair, which together comprise a DRAM cell. The capacitor holds a high or low charge (1 or 0, respectively), and the transistor acts as a switch that lets the control circuitry on the chip read the capacitor's state of charge or change it. As this form of memory is less expensive to produce than static RAM, it is the predominant form of computer memory used in modern computers.
Solid-state drive:
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies as memory to store data persistently. It is also sometimes called solid-state disk,[1] although SSDs do not have physical disks. SSDs may use traditional hard disk drive (HDD) form-factors and protocols such as SATA and SAS, greatly simplfying usage of SSDs in computers.[2] Following the initial acceptance of SSDs with HDD interfaces, new form factors such as the M.2 form factor, and new I/O protocols such as NVM Expresshave been developed to address specific requirements of the Flash memory technology used in SSDs.
Hard disk drive:
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk,[b] is an electromechanical data storage device that uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve digital information using one or more rigid rapidly rotating disks (platters) coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces.[2] Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored or retrieved in any order and not only sequentially. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data even when powered off.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario